Introduction
Physiotherapy is a vital component of the healthcare system, focusing on restoring and maintaining physical function and mobility. This field offers numerous specializations, each addressing specific patient needs. In this comprehensive blog, we will explore the different specializations within physiotherapy, including pediatric, geriatric, orthopedic, neurological, and cardiovascular physiotherapy. Whether you’re a student considering a career in physiotherapy or a patient seeking specialized care, understanding these specializations can help you make informed decisions. College Forum, the best platform for finding top colleges, can guide you in choosing the right institution for your physiotherapy education.
1. Pediatric Physiotherapy
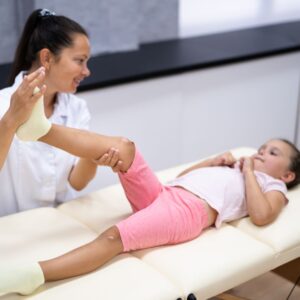
Overview: Pediatric physiotherapy deals with the assessment and treatment of infants, children, and adolescents who have physical impairments or disabilities. It aims to enhance their development and facilitate optimal functional independence. This specialization is crucial for addressing early-life physical challenges that, if left untreated, could impact a child’s growth and development.
Common Conditions Treated:
- Cerebral palsy
- Developmental delays
- Muscular dystrophy
- Spina bifida
- Torticollis
- Down syndrome
- Autism spectrum disorders
Techniques and Approaches:
- Play Therapy: Utilizes play to engage children in exercises and activities that improve motor skills and coordination. Play therapy makes the rehabilitation process enjoyable and less intimidating for children, encouraging participation.
- Hydrotherapy: Water-based exercises that help in strengthening muscles and improving joint mobility. The buoyancy of water reduces stress on the joints, making movement easier for children with mobility issues.
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques to manipulate muscles and joints. These techniques can help improve muscle tone, reduce spasticity, and enhance overall mobility.
- Assistive Devices: Use of braces, walkers, and customized equipment to aid mobility. Properly selected and fitted assistive devices can significantly improve a child’s ability to move and interact with their environment.
- Sensory Integration Therapy: Techniques to help children with sensory processing issues improve their ability to respond to sensory stimuli.
Role of Pediatric Physiotherapists: Pediatric physiotherapists work closely with families, educators, and healthcare providers to create comprehensive treatment plans. They focus on improving a child’s physical abilities, confidence, and overall quality of life. Their role is not just therapeutic but also educational, providing parents and caregivers with strategies to support the child’s development at home.
Case Study: Consider a child with cerebral palsy who has difficulty walking. A pediatric physiotherapist would assess the child’s specific needs, develop a tailored exercise program, and work on improving strength, balance, and coordination. Over time, the child might transition from using a walker to walking independently, greatly enhancing their quality of life.
2. Geriatric Physiotherapy

Overview: Geriatric physiotherapy specializes in addressing the unique needs of elderly patients. As people age, they often face various physical challenges that can impact their independence and quality of life. This specialization aims to improve mobility, manage pain, and enhance the overall well-being of older adults.
Common Conditions Treated:
- Arthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Parkinson’s disease
- Stroke
- Post-surgical recovery
- Balance disorders
- Chronic pain
Techniques and Approaches:
- Strength Training: Exercises to maintain and improve muscle strength. Maintaining muscle mass and strength is crucial for the elderly to perform daily activities and prevent falls.
- Balance and Coordination Exercises: Activities to prevent falls and improve stability. Fall prevention is a critical aspect of geriatric physiotherapy, as falls are a leading cause of injury among the elderly.
- Pain Management Techniques: Methods like heat/cold therapy, ultrasound, and electrotherapy to manage chronic pain. Effective pain management allows elderly patients to participate more fully in rehabilitation and daily activities.
- Mobility Aids: Assessment and recommendation of walking aids, wheelchairs, and other assistive devices. Proper use of mobility aids can significantly enhance an elderly person’s ability to move safely and independently.
- Functional Training: Exercises that mimic daily activities to improve the ease of performing everyday tasks.
- Education: Teaching patients and caregivers about safe movement practices, home modifications, and lifestyle changes to support aging in place.
Role of Geriatric Physiotherapists: These specialists develop individualized treatment plans to enhance mobility, reduce pain, and increase functional independence. They also educate patients and caregivers on safe practices and preventive measures. Geriatric physiotherapists play a crucial role in helping elderly patients maintain their dignity and independence.
Case Study: An elderly patient recovering from hip replacement surgery might work with a geriatric physiotherapist to regain strength and mobility. The therapist would design a personalized rehabilitation program focusing on exercises to strengthen the hip and surrounding muscles, improve balance, and safely resume daily activities.
3. Orthopedic Physiotherapy

Overview: Orthopedic physiotherapy focuses on the musculoskeletal system, treating injuries and conditions related to bones, joints, ligaments, and muscles. It’s essential for recovery from injuries, surgeries, and chronic musculoskeletal conditions. This specialization is often associated with sports injuries but also addresses issues arising from everyday activities and aging.
Common Conditions Treated:
- Fractures
- Sprains and strains
- Back and neck pain
- Post-operative rehabilitation (e.g., joint replacement)
- Sports injuries
- Tendonitis
- Bursitis
Techniques and Approaches:
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as joint mobilization and manipulation to restore movement. These techniques help to alleviate pain, reduce stiffness, and improve joint function.
- Exercise Therapy: Customized exercise programs to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. Exercise therapy is tailored to the specific needs and goals of each patient.
- Modalities: Use of ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and heat/cold therapy for pain relief and tissue healing. These modalities can enhance the effectiveness of other treatment methods.
- Ergonomic Advice: Guidance on proper posture and movement to prevent injury. This is particularly important for patients whose work or daily activities place them at risk for musculoskeletal problems.
- Postural Training: Exercises and techniques to correct poor posture that contributes to pain and dysfunction.
- Sports Rehabilitation: Specialized programs to help athletes recover from injuries and return to their sport safely and effectively.
Role of Orthopedic Physiotherapists: Orthopedic physiotherapists design and implement rehabilitation programs to restore function, reduce pain, and prevent re-injury. They often work with athletes, post-surgical patients, and individuals with chronic musculoskeletal conditions. Their goal is to help patients return to their normal activities as quickly and safely as possible.
Case Study: A professional athlete who has suffered an ACL tear might undergo surgery followed by extensive rehabilitation with an orthopedic physiotherapist. The rehabilitation program would include strength training, balance exercises, and sport-specific drills to ensure the athlete can return to their sport at their pre-injury level.
4. Neurological Physiotherapy

Overview: Neurological physiotherapy addresses disorders of the nervous system, helping patients manage and recover from neurological conditions. It focuses on restoring movement patterns, improving functional abilities, and enhancing quality of life. This specialization requires a deep understanding of how neurological disorders affect the body and the best approaches to rehabilitate affected individuals.
Common Conditions Treated:
- Stroke
- Multiple sclerosis
- Parkinson’s disease
- Spinal cord injuries
- Traumatic brain injuries
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Cerebral palsy
Techniques and Approaches:
- Neurodevelopmental Treatment (NDT): Techniques to promote normal movement patterns. This approach helps patients improve their functional abilities through task-specific training.
- Bobath Approach: A holistic approach to improve motor control and coordination. The Bobath approach emphasizes the importance of quality of movement and aims to enhance postural control.
- Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT): Encourages use of the affected limb by restricting the unaffected limb. This technique is particularly effective for stroke rehabilitation.
- Balance and Coordination Training: Exercises to improve stability and prevent falls. Enhancing balance and coordination is crucial for patients with neurological impairments.
- Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): Use of electrical currents to stimulate muscle contractions and improve motor function.
- Gait Training: Techniques to improve walking ability and efficiency.
Role of Neurological Physiotherapists: These specialists develop personalized treatment plans to maximize recovery and functional independence. They use evidence-based practices to help patients regain as much mobility and function as possible. Neurological physiotherapists often work as part of a multidisciplinary team, collaborating with neurologists, occupational therapists, and speech therapists to provide comprehensive care.
Case Study: A patient recovering from a stroke might work with a neurological physiotherapist to regain motor function and coordination. The therapist would use techniques like CIMT to encourage use of the affected limb, balance exercises to improve stability, and gait training to restore walking ability.
5. Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physiotherapy

Overview: Cardiovascular and pulmonary physiotherapy focuses on patients with heart and lung conditions. It aims to improve cardiovascular fitness, respiratory function, and overall health. This specialization plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation of patients who have undergone cardiac or pulmonary surgeries, as well as those with chronic conditions affecting the heart and lungs.
Common Conditions Treated:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Asthma
- Post-heart surgery rehabilitation
- Cystic fibrosis
- Congestive heart failure
- Coronary artery disease
- Pulmonary fibrosis
Techniques and Approaches:
- Breathing Exercises: Techniques to improve lung capacity and efficiency. These exercises help patients manage breathlessness and enhance their ability to perform daily activities.
- Aerobic Training: Activities to enhance cardiovascular fitness and endurance. Aerobic training improves heart health and overall stamina.
- Chest Physiotherapy: Methods like postural drainage, percussion, and vibration to clear respiratory secretions. These techniques are essential for patients with conditions that cause excessive mucus production.
- Education and Lifestyle Modification: Guidance on healthy lifestyle choices, including diet and exercise. Education helps patients understand their condition and manage it effectively.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programs: Comprehensive programs that include exercise, education, and support to improve respiratory function.
- Functional Training: Exercises to improve the ability to perform daily activities without excessive fatigue or breathlessness.
Role of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physiotherapists: These specialists create tailored exercise programs to improve respiratory and cardiovascular health. They work closely with patients to manage symptoms, increase physical activity, and improve overall quality of life. Cardiovascular and pulmonary physiotherapists often work in hospital settings, outpatient clinics, and specialized rehabilitation centers.
Case Study: A patient recovering from coronary artery bypass surgery might work with a cardiovascular physiotherapist to gradually regain strength and endurance. The rehabilitation program would include monitored aerobic exercises, strength training, and education on lifestyle changes to support heart health.
Conclusion
Physiotherapy encompasses a wide range of specializations, each catering to different patient needs and conditions. Understanding these specializations can help individuals seek the appropriate care and allow aspiring physiotherapists to choose a career path that aligns with their interests and goals. For students considering a career in physiotherapy, College Forum is the best platform to find the best colleges, including those in Dehradun, offering excellent education and training in various physiotherapy specializations.
By choosing the right institution, students can gain the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in their chosen field and make a significant impact on their patients’ lives. Whether you’re interested in pediatric, geriatric, orthopedic, neurological, or cardiovascular physiotherapy, the journey starts with selecting the right college, and College Forum is here to guide you every step of the way.

